A guide to using SETTE
Overview
SETTE is a suite of bash scripts that automates the building, running and
basic validation and verification of a broad spectrum of NEMO reference and
test configurations. Because compilation and batch running environments differ
wildly, automation is only achieved after some effort by the user for each new test
platform. However, examples are provided for all the major systems used by the NEMO
System team and many new platforms can be incorporated simply by adapting these
templates.
When configured correctly, a single command will:
Compile multiple reference and test configurations
Run restartability and reproducibility tests with each configuration
Run additional conformance checks with any AGRIF-based configurations
Archive sufficient output measures for meaningful comparsion between future tests at different revisions
On completion, run a secondary script to table the successes or failures of each test
Many namelist-controlled options can be varied using command line arguments to the main sette script and test results can be compared across different innvocations. Thus, by chaining sette innvocations with different options, more complex and comprehensive testing can be achieved.
Installation
SETTE is provided within the main NEMO git repository and will be found in the
subdirectory sette below the top-level of a checked out (cloned) copy (at the same
level as src/ or cfgs/).
Initial setup
Assuming, for now, that you are intending to run SETTE on one of the platforms
already supported then there are only a few settings required to setup for each
individual user. These settings are all to be found in the sette/param.default file:
NEMO_VALIDATION_REF=/path/to/reference/sette/results
NEMO_REV_REF=0000
COMPILER=${SETTE_COMPILER:-XXXXXXXX}
BATCH_CMD=${SETTE_BATCH_CMD:-llsubmit}
BATCH_STAT=${SETTE_BATCH_STAT:-llq}
FORCING_DIR=${SETTE_FORCING_DIR:-$WORKDIR/FORCING}
NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR=${SETTE_NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR:-$MAIN_DIR}/NEMO_VALIDATION
JOB_PREFIX_NOMPMD=${SETTE_JOB_PREFIX_NOMPMD:-batch}
JOB_PREFIX_MPMD=${SETTE_JOB_PREFIX_MPMD:-batch-mpmd}
and each can be set either in a param.cfg file (created by copying param.default
to param.cfg and editing) or through the corresponding environment variable. For
example, changing the contents of a param.cfg to include:
NEMO_VALIDATION_REF=/work/n01/n01/acc/NEMO/2024/5.0.0/sette/NEMO_VALIDATION
NEMO_REV_REF=24335_c1604aac
COMPILER=X86_ARCHER2-Cray
BATCH_CMD=sbatch
BATCH_STAT=squeue
FORCING_DIR=/work/n01/n01/acc/FORCING/SETTE_inputs/5.0.0
NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR=/work/n01/n01/acc/NEMO/2024/5.0.0/sette/NEMO_VALIDATION
JOB_PREFIX_NOMPMD=batch
JOB_PREFIX_MPMD=batch
or settings:
export SETTE_COMPILER=X86_ARCHER2-Cray
export SETTE_BATCH_CMD=sbatch
export SETTE_BATCH_STAT=squeue
export SETTE_FORCING_DIR=/work/n01/n01/acc/FORCING/SETTE_inputs/5.0.0
export SETTE_NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR=/work/n01/n01/acc/NEMO/2024/5.0.0/sette/NEMO_VALIDATION
export SETTE_JOB_PREFIX_NOMPMD=batch
export SETTE_JOB_PREFIX_MPMD=batch
in your runtime environment will achieve the same result. The requirement to create a
param.cfg from param.default for each installation protects against developers
accidentally returning a local param.cfg to the main repository. The param.default
file should only be altered by SETTE developers.
Note
Apart from NEMO_VALIDATION_REF and NEMO_REV_REF which do not have an equivalent environment variable - TO BE FIXED
The purposes of these settings should be clear:
NEMO_VALIDATION_REFpoints to aSETTE-generated directory of previous archived results to be used optionally as a reference set.NEMO_REV_REFdefines the reference tag (since raw git commit hashes do not list chronologically, they are prepended with a string constructed from the year and year-day)COMPILERnames the architecture file to be used to compile NEMOBATCH_CMDnames the command used to submit jobs to the batch systemBATCH_STATnames the command used to query the batch system and return a list of queued and running jobsFORCING_DIRpoints to a directory containing the input files required by the reference configurations. Details of how to obtain the files with which to populate this directory are provided in the Obtaining configuration input files section. Note that this directory must be in a part of the filesystem that is visible to the back-end compute nodes.NEMO_VALIDATION_DIRpoints to a directory under whichSETTEwill archive its results.JOB_PREFIX_NOMPMDA prefix for the template batch file if running in SPMD mode (e,g. with attached XIOS servers)JOB_PREFIX_MPMDAn alternative prefix for the template batch file if running in MPMD mode (i.e. with detached XIOS servers). This isn’t necessarily different to the SPMD setting since some of the templates provided are written to handle both modes. See the Template batch files section for details.
Obtaining configuration input files
Many of the reference configurations require domain files, initial conditions and surface
forcing fields. The exceptions are the GYRE_PISCES configurations and the simpler,
test-cases. It is possible to limit SETTE to a subset of tests to avoid the need for
downloading data files but far less of the code will be covered by the tests in this case.
All the required files are available from the SETTE inputs site .
The entire set of inputs can be downloaded using the ./sette_fetch_inputs.sh script
which uses wget to retrieve the files and populate the FORCING_DIR directory.
I.e.:
sette_fetch_inputs.sh -h
sette_fetch_inputs.sh :
Fetch 5.0.0 input files from remote store
Template batch files
If you have previously compiled NEMO successfully on your test platform then you can have
confidence that providing the same environment and arch file to SETTE will allow SETTE
to compile successfully (barring any compile-time bugs in previously untested code).
However, SETTE also needs to configure and run a series of batch jobs with varying
resource requirements. To do this, you must provide SETTE with a means to generate valid
job submission scripts. There are essentially two ways of doing this:
Provide a template batch file with known strings that
SETTEcan replace with settings based on the needs of each job.Provide an external script that can accept those settings and generate a new batch file.
If you are working on a test platform already supported by SETTE, a solution will already
be in place and you can skip to the Component scripts section.
If you are commissioning a new platform then you will need to provide either a template
batch file or an external generating script. Batch file templates are located in the
sette/BATCH_TEMPLATE subdirectory. They are named with the COMPILER setting
prefixed by the JOB_PREFIX_NOMPMD (or JOB_PREFIX_NOMPMD) setting and separated by
a hyphen. To use the first method, the batch template should be a version of a working
submission script with the following strings in place of their corresponding numerical
values:
NODES The total number of nodes required
TOTAL_NPROCS The total number of cores required
NPROCS The number of ocean cores
NXIOPROCS The number of XIOS cores
MPI_FLAG A logical to declare if MPI is being used
DEF_EXE_DIR The test execution directory
Paths and names that have to be passed through
to the post-run tidy-up script:
DEF_SETTE_DIR
DEF_INPUT_DIR
DEF_CONFIG_DIR
DEF_TOOLS_DIR
DEF_NEMO_VALIDATION
DEF_NEW_CONF
DEF_CMP_NAM
DEF_TEST_NAME
Not all of these need to used and if your particular system needs additional information then this
can be added as a case statement (dependent on COMPILER) in the prepare_job.sh script
An example template file is given in the sette_batch_template file:
cat BATCH_TEMPLATE/sette_batch_template
#!/bin/bash
#!
# @ job_name = MPI_config
# standard output file
# @ output = $(job_name).$(jobid)
# standard error file
# @ error = $(job_name).$(jobid)
# job type
# @ job_type = parallel
# Number of procs
# @ total_tasks = NPROCS
# time
# @ wall_clock_limit = 0:30:00
# @ queue
#
# Test specific settings. Do not hand edit these lines; the prepare_job.sh script will set these
# (via sed operating on this template job file).
#
OCEANCORES=NPROCS
export SETTE_DIR=DEF_SETTE_DIR
###############################################################
#
# set up mpp computing environment
#
# Local settings for machine IBM Power6 (VARGAS at IDRIS France)
#
export MPIRUN="mpiexec -n $OCEANCORES"
#
# load sette functions (only post_test_tidyup needed)
#
. ${SETTE_DIR}/all_functions.sh
# Do not remove or change the following comment line
# BODY
#
# These variables are needed by post_test_tidyup function in all_functions.sh
#
export EXE_DIR=DEF_EXE_DIR
export INPUT_DIR=DEF_INPUT_DIR
export CONFIG_DIR=DEF_CONFIG_DIR
export TOOLS_DIR=DEF_TOOLS_DIR
export NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR=DEF_NEMO_VALIDATION
export NEW_CONF=DEF_NEW_CONF
export CMP_NAM=DEF_CMP_NAM
export TEST_NAME=DEF_TEST_NAME
#
# end of set up
###############################################################
#
# change to the working directory
#
cd ${EXE_DIR}
echo Running on host `hostname`
echo Time is `date`
echo Directory is `pwd`
#
# Run the parallel MPI executable
#
if [ MPI_FLAG == "yes" ]; then
echo "Running time ${MPIRUN} ./nemo"
time ${MPIRUN} ./nemo
else
echo "Running time./nemo"
time ./nemo
fi
#
post_test_tidyup
# END_BODY
# Do not remove or change the previous comment line
exit
But commamds and environments are most likely different on every test platform so it may require some effort to produce an equivalent template for new platforms.
For cases where the calculation and declaration of resources is more complex (for example, in hetrogeneous computing environments requiring het-job declarations), in may be easier to provide an external script to generate the job script. An example is included in the case of X86_ARCHER2-Cray where the batch template is simply a placeholder:
#!/bin/bash
#
# A batch script will be generated using:
# /work/n01/shared/acc/mkslurm_settejob -S $NXIO_PROC -s 8 -m 4 -C $NB_PROC -g 2 -a n01-CLASS -j sette_job -t 20:00 > ${SETTE_DIR}/job_batch_template
# by prepare_job.sh
#
and the suggested script is executed by prepare_job.sh instead of editing the template:
case ${COMPILER} in
X64_MOBILIS*)
.
.
;;
X86_ARCHER2*)
MK_TEMPLATE=$( /work/n01/shared/acc/mkslurm_settejob_4.2 -S $NXIO_PROC -s 8 -m 4 -C $NB_PROC -g 2 -a n01-CLASS -j sette_job -t 20:00 > ${SETTE_DIR}/job_batch_template )
;;
Any such solutions should be fed back to the system team for incorporation into future releases.
Component scripts
SETTE consists of a suite of scripts and settings files. A complete list is given here but basic
use of SETTE only requires familiarisation with the first two listed:
User scripts and settings
param.cfgsette.shsette_reference-configurations.shsette_test-cases.sh
sette_rpt.shsette_eval.shsette_fetch_inputs.shsette_list_avail_cfg.shsette_list_avail_rev.sh
Internal scripts and settings
all_functions.shfcm_job.shprepare_exe_dir.shprepare_job.shinput_<CONFIG>.cfg
Usage of main scripts
The purpose and contents of param.cfg were explained in the Initial setup section.
sette.sh is the main utility script that, when executed without any arguments, will
compile, configure and submit a pre-set series of tests. After all the tests have completed,
a basic report is presented to the user which lists the various successes or failures.
./sette.sh
<lots of progress information and compilation stages>
./sette_rpt.sh -V different_branch
SETTE validation report generated for :
branch_5.0 @ 5ac534cc (with local changes)
on ANEMONE-ifort23 arch file
!!---------------1st pass------------------!!
!----restart----!
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES tracer.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_OFF_PISCES tracer.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
AMM12 run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
AGRIF_DEMO run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
AGRIF_DEMO tracer.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
WED025 run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
GYRE_PISCES run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
GYRE_PISCES tracer.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_SAS_ICE run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
C1D_PAPA run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
SWG run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ICE_AGRIF run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
OVERFLOW run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
VORTEX run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ISOMIP+ run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
IWAVE run.stat restartability passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
!----repro----!
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES tracer.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_OFF_PISCES tracer.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
AMM12 run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
AGRIF_DEMO run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
AGRIF_DEMO tracer.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
WED025 run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
GYRE_PISCES run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
GYRE_PISCES tracer.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_SAS_ICE run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_ICE_OBS run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_ICE_OBS obs.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
SWG run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ICE_AGRIF run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
VORTEX run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
ISOMIP+ run.stat reproducibility passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
!----transform----!
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_OFF_PISCES transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
AMM12 transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
AGRIF_DEMO transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
WED025 transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
GYRE_PISCES transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_SAS_ICE transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
ORCA2_ICE_OBS transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
C1D_PAPA transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
SWG transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
ICE_AGRIF transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
OVERFLOW transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
VORTEX transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
ISOMIP+ transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
IWAVE transformed variants MISSING : 24341_5ac534cc+
!----phyopt----!
OVERFLOW/sco_FCT2_flux_cen-ahm1000 ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
OVERFLOW/sco_FCT2_flux_ubs ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
OVERFLOW/zps_FCT2_flux_ubs ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
OVERFLOW/sco_FCT4_flux_cen-ahm1000 ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
OVERFLOW/sco_FCT4_flux_ubs ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
OVERFLOW/zps_FCT4_flux_ubs ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
OVERFLOW/zps_FCT4_vect_een ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT2_flux_cen2 ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT2_vect_ene ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT2_vect_ens ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT2_vect_een ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT2_flux_ubs ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT2_vect_eenH ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT4_flux_cen2 ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT4_vect_ene ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT4_vect_een ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT4_flux_ubs ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT4_vect_eenH ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
LOCK_EXCHANGE/FCT4_vect_ens ocean.output phyopts passed : 24341_5ac534cc+
!----agrif check----!
ORCA2 AGRIF vs ORCA2 NOAGRIF run.stat unchanged passed : 24341_5ac534cc+ 24341_5ac534cc+
!----result comparison check----!
check result differences between :
VALID directory : /dssgfs01/scratch/acc/branches/pre_release_5.0/sette/NEMO_VALIDATION/branch_5.0 at rev 24341_5ac534cc+
and
REFERENCE directory : /dssgfs01/scratch/acc/branches/pre_release_5.0/sette/NEMO_VALIDATION/different_branch at rev 24332_16c60ec5+
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES run.stat files are DIFFERENT (results are different after 1 time steps) (LONG)
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES tracer.stat files are DIFFERENT (results are different after 1 time steps) (LONG)
Report timing differences between REFERENCE and VALID (if available) :
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES ref. time: 263.349203 cur. time: 211.858526 diff.: -51.4907
The report shows the result of restartability and reproducibility tests on the whole range of test configurations. Passing the default set of tests is a necessary and mandatory requirement for any official release of NEMO. Note these tests are not sufficient to guarantee restartability and reproducibility in all user-defined configrations and anyone running configurations, which are not close variants of the reference or test configurations, should conduct their own tests.
SETTE will also carry out tests with alternative physics options that are defined for some configurations,
and optionally tests on PSyclone-based code transformations. The range of tests carried out
can be varied via the -x command-line option to sette.sh. The default set of tests is equivalent to
sette.sh -x "COMPILE RESTART REPRO CORRUPT PHYOPTS"
and optionally the SETTE test option TRANSFORM can be included in the argument to enable the testing of
PSyclone-based code transformations (this includes a comparison of model results and runtimes between model
runs based on untransformed and transformed code). This report ends by comparing the latest results against
a reference set (as defined in param.cfg). Only ORCA2_ICE_PISCES had been run on the alternative branch and the
missing comparisons have been omitted here. In this case the comparison is between
branches that were known to introduce numerical differences. This is confined by the
comparsion but the report is most useful when numerical results are not expected to change
between revisions and when changes are expected to provide a performance benefit. It is
not shown here but, on many terminals, test failures or performance drops are presented in
red to highlight areas of concern.
The set of tests executed by default are set in param.cfg in the TEST_CONFIGS
environment variable:
grep TEST_CONFIG_AVAIL param.default
TEST_CONFIG_AVAILABLE=(ORCA2_ICE_PISCES ORCA2_OFF_PISCES AMM12 AGRIF_DEMO WED025 GYRE_PISCES ORCA2_SAS_ICE ORCA2_ICE_OBS C1D_PAPA SWG ICE_AGRIF OVERFLOW LOCK_EXCHANGE VORTEX ISOMIP+ IWAVE)
export TEST_CONFIGS=(${SETTE_TEST_CONFIGS[@]:-${TEST_CONFIG_AVAILABLE[@]}})
Note this set can be overridden by externally setting the SETTE_TEST_CONFIGS
environment variable but individual or sub-sets of tests can also be selected by arguments
to the -n option to sette.sh. This is more explicit and the recommended method since
release 4.2.
Other options to sette.sh can be listed using the -h argument:
./sette.sh -h
sette.sh with no arguments (in this case all configuration will be tested with default options)
-T to set ln_timing false for configurations (default: true)
-t set ln_tile false in all tests that support it (default: true)
-e set nn_hls=3 but it is not yet supported (default: nn_hls=2)
-i set ln_icebergs false (default: true)
-a set ln_abl true (default: false)
-C set nn_comm=1 (default: nn_comm=2 ==> use MPI3 collective comms)
-N set ln_nnogather false for ORCA2 configurations (default: true)
-q to remove the key_qco key (default: added)
-X to remove the key_xios key (default: added)
-Q to remove the key_RK3 key
-A to run tests in attached (SPMD) mode (default: MPMD with key_xios)
-n "CFG1_to_test CFG2_to_test ..." to test some specific configurations
-x "TEST_type TEST_type ..." to specify particular type(s) of test(s) to run after compilation
TEST_type choices are: COMPILE RESTART REPRO CORRUPT PHYOPTS TRANSFORM
-v "subdir" optional validation record subdirectory to be created below NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR
-g "group_suffix" single character suffix to be appended to the standard _ST suffix used
for SETTE-built configurations (needed if sette.sh invocations may overlap)
-r to execute without waiting to run sette_rpt.sh at the end (useful for chaining sette.sh invocations)
-y to perform a dryrun to simply report what settings will be used
-b to compile Nemo with debug options (only if %DEBUG_FCFLAGS if defined in your arch file)
-c to clean each configuration
-s to synchronise the sette MY_SRC and EXP00 with the reference MY_SRC and EXPREF
-w to wait for Sette jobs to finish
-r to print Sette report after Sette jobs completion
-u to run sette.sh without any user interaction. This means no checks on creating
directories etc. i.e. no safety net!
The first 11 options are switches to toggle commonly used namelist options or compile time
keys. The default setting is to have the option set .true. or the corresponding key
added. Thus, for example, running:
./sette.sh -i -Q
will run the full suite without icebergs (i.e. ln_icebergs=.false.) and without
key_RK3 added at compile time. Some of these options (-i, for example)
will only affect those configurations that activate the related code option by default.
The -n option allows a sub-set of tests to be named on the command line. Testing will
be restricted to the named tests; multiple tests can be listed as a quoted,
space-separated string. For example:
./sette.sh
and
./sette.sh -n "ORCA2_ICE_PISCES ORCA2_OFF_PISCES AMM12 AGRIF_DEMO WED025 GYRE_PISCES ORCA2_SAS_ICE ORCA2_ICE_OBS C1D_PAPA SWG ICE_AGRIF OVERFLOW LOCK_EXCHANGE VORTEX ISOMIP+ IWAVE"
are equivalent. As a point of interest, it is good practise to list tests in decreasing order of their expected execution time. This will enable compilation time to overlap run-time as much as possible and should minimise time to completion
The default operation is to perform all RESTART, REPRO, AGRIF-processing
CORRUPT, and PHYOPTS (optional physical schemes) checks. The checks performed can be
limited to a sub-set of these by supplying arguments to the -x option. The combination of
-n and -x is particularly useful when working to solve a specific issue with a single
configuration. The optional TRANSFORM test enables the testing of PSyclone-based source-code
transformations. Any other string supplied as an argument to the -x
option will force a compilation only. This is useful for quickly checking for compile-time
errors. Although any non-recognised string will trigger this, it is good practise to be
explicit, i.e.:
./sette.sh -x COMPILE
The -s option forces a synchronisation of MY_SRC contents and input files from the
EXREF directory of the reference configuration on which the test is based. This is useful
if you know these contents have been changed but do not wish to enforce a complete rebuild.
The -c option forces a clean rebuild from scratch of the test configuration. The
*_ST? directory will be deleted and recreated before a complete compilation and run is
performed. Finally, the -u option disables any interaction with the user. By default,
sette.sh will request confirmation from the user for actions such as: creating the
base NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR or disabling options when incompatible choices are selected.
This interaction can be problematic with continuous integration systems and the -u
option should always be used in these applications. It is the responsibility of the user
to ensure that the correct information is provided to sette.sh in these cases.
The test results archive
This latest version of SETTE (released with NEMO v4.2) changes the organisation of the
records kept under the NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR. This is partly to accommodate the fact
that the new command-line options provide so much flexibility for running a series of
tests on any one revision of the code with different options. To facilitate such testing,
two new command-line options have been introduced: -v <subdir> and
-g <sub-group_suffix>.
-v names a sub-directory to create (or re-use) beneath NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR
as the root of the records tree. If the -v option is not used then root of the
directory tree will be the branch name as returned by the:
git branch --show-current
command (or MAIN if this command fails for any reason).
-g names a single character suffix that will be appended to the traditional _ST
suffix that is added to the configurations built for testing. I.e.:
./sette.sh -e -v HALO1 -g 0
will compile and run the full suite with nn_hls=1. The configurations will be
constructed with names such as: GYRE_PISCES_ST0 and the directory structure
eventually populated with the test records would be similar to:
./NEMO_VALIDATION
|-HALO1
|---X86_ARCHER2-Cray
|-----21334_a2c5986+
|-------AGRIF_DEMO
|---------LONG
|---------ORCA2
|---------REPRO_2_8
|---------REPRO_4_4
|---------SHORT
|-------AGRIF_DEMO_NOAGRIF
|---------ORCA2
|-------AMM12
|---------LONG
|---------REPRO_4_8
|---------REPRO_8_4
|---------SHORT
|-------GYRE_PISCES
|---------LONG
|---------REPRO_2_4
|---------REPRO_4_2
|---------SHORT
.
.
.
Use of the -g option isn’t always necessary. In this case, for example, -e
only triggers a namelist changes so there is no difference in the compiled code between
this set and the default set (which will use names such as GYRE_PISCES_ST and would
have records stored under branch-name). Thus, running tests sequentially such as:
./sette.sh
./sette.sh -e -v HALO1
will reuse the same run-time directories and only require one set of compilations.
However, it will not be possible to diagnose any issues with the first set after the
second has run. The use of -g is recommended when running multiple tests with
different compilation keys since future tests with updated code may only need to
recompile changed modules and dependencies.
Note also that the move from subversion to git forces a change in the revision
tag used to identify the code base being tested. Whereas, with subversion, the revision
number was a integer that increased monotonically in the time-order of commits, git
identifies its commits with long, hexadecimal hash strings that are not necessarily
correctly time-ordered when listed alphanumerically. The:
git rev-list --abbrev-commit -1 origin
command can be used to obtain a abbreviated commit hash that still provides a unique
identifier but extra steps are required to provide a revision_tag that retains some
indication of time-order. The current solution is to prepend the abbreviated hash string
with a representation of the date on which the commit was made. This information can
be obtained from the git log response as follows:
git log -1 | grep Date | sed -e 's/.*Date: *//' -e's/ +.*$//'
Mon Dec 6 15:24:36 2021
Condensing this string into something usable requires use of the unix date command
which can vary in different flavours of the OS. Two examples are currently supported,
one for MacOSX and one, more general, POSIX variety. More can be added in param.cfg
as required. Each supported style is tested in param.cfg to determine which form to use:
# command for converting date (from git log -1) into 2-digit year + yearday
#
date -j -f "%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y" "Tue Nov 30 17:10:53 2021" +"%y%j" >& /dev/null
if [ $? == 0 ] ; then DATE_CONV='date -j -f "%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y" ' ;fi
#
date --date="Tue Nov 30 17:10:53 2021" +"%y%j" >& /dev/null
if [ $? == 0 ] ; then DATE_CONV='date --date=' ;fi
In both cases, the output format is a 2-digit year + a 3-digit year-day resulting in a 5-digit string to prepend to the short hash. There is still scope for slight mis-ordering between commits committed on the same day but this compromise avoids over-long revision tags.
In the example directory listing above the revision tag is shown as: 21334_a2c5986+
which displays a typical 5-digit date and 7-digit short hash separated by an underscore.
In this case a + has been appended because sette has detected local changes to
the base commit. The output of:
git status --short -uno
is used to check for local modifications when making this decision.
Super-sized SETTE
The idea of chaining a series of tests to test various options leads to the possibility of
a super_sette.sh script. For example, this content:
#!/bin/bash
# set -vx
# Simple script to robustly run a full suite of SETTE tests
#
########################################
# Start of main script
########################################
FULLSET=( ORCA2_ICE_PISCES ORCA2_OFF_PISCES AMM12 AGRIF WED025 GYRE_PISCES SAS ORCA2_ICE_OBS SWG ICE_AGRIF OVERFLOW LOCK_EXCHANGE VORTEX ISOMIP+ )
#
GROUP_SETS=( "-g 0 -r -v MAIN" "-e -F -t -g 1 -v HALO1 -r" "-q -g 2 -v NO_QCO -r" "-i -e -F -t -g 3 -v NO_ICB1 -r" "-i -g 4 -v NO_ICB2 -r" "-C -g 5 -v NO_COLL -r" )
#
# These groups sets correspond to the following test regimes:
#
# A. Three complete sets with various combinations of options:
#
printf "%-93s %s\n" "Full tests - MAIN with default options (using *_ST0 config dirs) : " "${GROUP_SETS[0]}"
printf "%-93s %s\n" "Full tests - HALO1 with nn_hls=1 (no tiling or loop fusion) (using *_ST1 config dirs) : " "${GROUP_SETS[1]}"
printf "%-93s %s\n" "Full tests - NO_QCO without qco (using *_ST2 config dirs) : " "${GROUP_SETS[2]}"
#
# B. Three different option choices with ORCA2_ICE_PISCES only:
#
printf "%-93s %s\n" "ORCA2_ICE_PISCES tests - NO_ICB1 without icebergs, with nn_hls=1 (using *_ST3 config dirs) : " "${GROUP_SETS[3]}"
printf "%-93s %s\n" "ORCA2_ICE_PISCES tests - NO_ICB2 without icebergs, with nn_hls=2 (using *_ST4 config dirs) : " "${GROUP_SETS[4]}"
printf "%-93s %s\n" "ORCA2_ICE_PISCES tests - NO_COLL without collective comms (using *_ST5 config dirs) : " "${GROUP_SETS[5]}"
#
# A. Full tests
for gs in 0 1 2
do
for n in `seq 0 1 $(( ${#FULLSET[@]} - 1 ))`
do
confstr="${FULLSET[$n]}"
# run the test
echo ./sette.sh ${GROUP_SETS[$gs]} -x "RESTART REPRO CORRUPT" -n "$confstr"
./sette.sh ${GROUP_SETS[$gs]} -x "RESTART REPRO CORRUPT" -n "$confstr"
done
done
#
# B. ORCA2_ICE_PISCES special tests
for gs in 3 4 5
do
# run the test
echo ./sette.sh ${GROUP_SETS[$gs]} -x "RESTART REPRO" -n ORCA2_ICE_PISCES
./sette.sh ${GROUP_SETS[$gs]} -x "RESTART REPRO" -n ORCA2_ICE_PISCES
done
exit
will perform all these tests:
Full tests - MAIN with default options (using *_ST0 config dirs) : -g 0 -r
Full tests - HALO1 with nn_hls=1 (no tiling or loop fusion) (using *_ST1 config dirs) : -e -F -t -g 1 -v HALO1 -r
Full tests - NO_QCO without qco (using *_ST2 config dirs) : -q -g 2 -v NO_QCO -r
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES tests - NO_ICB1 without icebergs, with nn_hls=1 (using *_ST3 config dirs) : -i -e -F -t -g 3 -v NO_ICB1 -r
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES tests - NO_ICB2 without icebergs, with nn_hls=2 (using *_ST4 config dirs) : -i -g 4 -v NO_ICB2 -r
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES tests - NO_COLL without collective comms (using *_ST5 config dirs) : -C -g 5 -v NO_COLL -r
and create archive structures under: MAIN, HALO1, NO_QCO, NO_ICB1,
NO_ICB2, NO_COLL subdirectories. An new command-line option: -r has been
introduced and used here. It simply prevents the sette.sh from generating a report on
completion. Normally, sette.sh waits until all jobs have completed and then runs the
sette_rpt.sh script to produce the report. When chaining invocations like this there
is no requirement to produce a report between invocations and therefore no need to wait
for individual jobs to complete. sette_rpt.sh can always be invoked directly, see
section: Reporting options for more details.
Archive contents
SETTE places copies of selected output files from each test within the relevant
subdirectory of the results directory structure. The selection of files is sufficient for
simple comparsions between equivalent tests carried out with different code revisions,
different run-time options or different compile-time keys. An example full set is:
ls -1 NEMO_VALIDATION/HALO1/X86_ARCHER2-Cray/24335_c1604aac+/ORCA2_ICE_PISCES/LONG
namelist_cfg
namelist_ice_cfg
namelist_pisces_cfg
namelist_top_cfg
ocean.output
output.namelist.dyn
output.namelist.ice
output.namelist.pis
output.namelist.top
run.stat
sette_config
timing.output
tracer.stat
but some tests may have fewer files (e.g. not all tests runs will produce a
tracer.stat file and timing information may not have been requested).
NOTE: we should add the run.stat.nc files as well
The main comparison is performed between run.stat and tracer.stat files and
any differences will be highlighted. ocean.output files and the input namelists are
included to enable verification of the actual runtime conditions. The output namelists
are also included so that accurate reading of the namelists can be verified. A new
addition at release 4.2 is the sette_config file which is a record on the options used
for this particular invocation of sette.sh. For example:
cat ./NEMO_VALIDATION/dev_main_halos/X86_ARCHER2-Cray/21336_0235f28+/GYRE_PISCES/LONG/sette_config
Summary of sette environment
----------------------------
requested by the command : ./sette.sh -n GYRE_PISCES -u
on branch : dev_main_halos
USING_TIMING : yes
USING_ICEBERGS : yes
USING_EXTRA_HALO : yes
USING_TILING : yes
USING_COLLECTIVES : yes
USING_QCO : yes
USING_LOOP_FUSION : yes
USING_XIOS : yes
USING_MPMD : yes
USING_RK3 : no
USER_INPUT : no
Common compile keys added : key_xios key_loop_fusion key_qco
Common compile keys deleted : key_RK3
Compile keys actually used : key_top key_linssh key_xios key_loop_fusion
Reporting options
As mentioned previously, the reporting function is performed by the sette_rpt.sh
script. This is normally invoked by sette.sh but can be run at anytime. The script
accepts several command-line options which makes it a versatile tool for comparing across
different sets of tests:
./sette_rpt.sh -h
sette_rpt.sh :
display result for the latest change
-c COMPILER_name :
display result for the specified compiler
-r REVISION_number :
display sette results for the specified revision (set old for the latest revision available for each config)
-R REFERENCE REVISION_number :
compare sette results against the specified revision (use to over-ride value set in param.cfg)
-v sub_dir :
validation sub-directory below NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR
-V sub_dir2 :
2nd validation sub-directory below NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR
if set the comparison is between two subdirectory trees beneath NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR
-u to run sette_rpt.sh without any user interaction
sette_rpt.sh will check all restartability and reproducibility results as well as
comparing differences between sets. A stripped down version is available
named:sette_eval.sh which can be used for a quick evaluation of differences only. For
example:
./sette_eval.sh -V MAIN -v HALO1 -R 14886
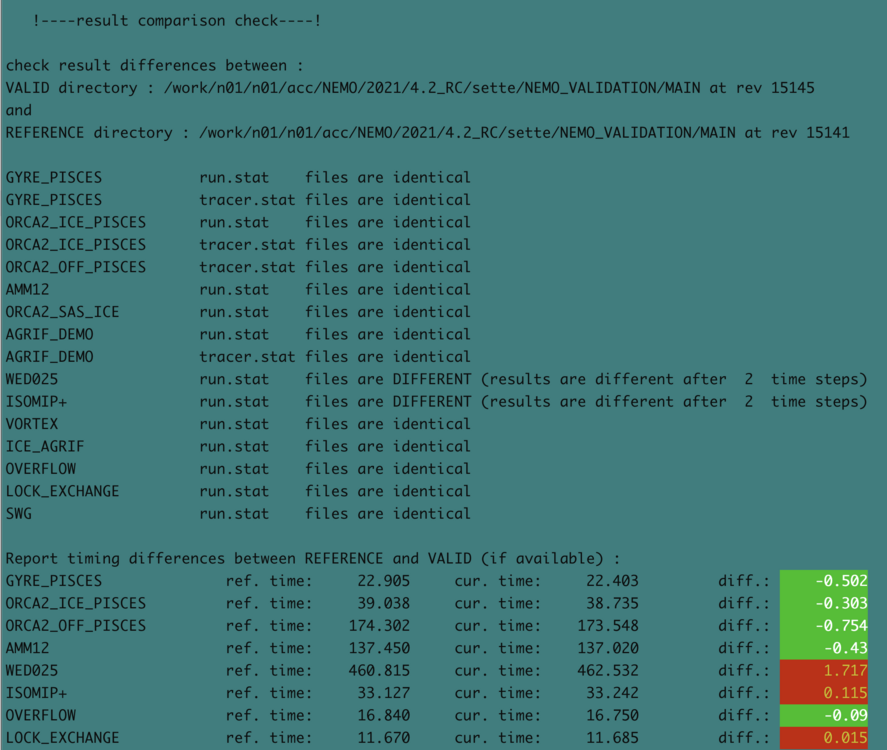
Current code is : NEMO/trunk @ r14896 ( last change @ r14886 )
SETTE evaluation for :
NEMO/trunk @ r14886 (last changed revision)
on X86_ARCHER2-Cray arch file
!----result comparison check----!
check result differences between :
VALID directory : /work/n01/n01/acc/NEMO/2021/midmerge/dev_sette/NEMO_VALIDATION/HALO1 at rev 14886
and
REFERENCE directory : /work/n01/n01/acc/NEMO/2021/midmerge/dev_sette/NEMO_VALIDATION/MAIN at rev 14886
GYRE_PISCES run.stat files are identical
GYRE_PISCES tracer.stat files are identical
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES run.stat files are DIFFERENT (results are different after 71 time steps)
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES tracer.stat files are DIFFERENT (results are different after 73 time steps)
ORCA2_OFF_PISCES tracer.stat files are DIFFERENT (results are different after 17 time steps)
AMM12 run.stat files are identical
ORCA2_SAS_ICE run.stat files are identical
AGRIF_DEMO run.stat files are identical
WED025 run.stat files are identical
ISOMIP+ run.stat files are identical
VORTEX run.stat files are identical
ICE_AGRIF run.stat files are identical
OVERFLOW run.stat files are identical
LOCK_EXCHANGE run.stat files are identical
SWG run.stat files are identical
This script also has a “quiet mode” for less verbose output (possibly, more suited for regular monitoring appliactions):
./sette_eval.sh -V MAIN -v HALO1 -R 14886 -q
3 differences from 13 matches.
It is also useful when tests have only been run with a few configurations. Take the
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES only tests suggested by super_sette.sh, for example:
./sette_eval.sh -V MAIN -v NO_ICB2 -R 14886 -q
2 differences from 1 matches. 0 missing from REFERENCE 12 missing from VALID
The two differences here being some run.stat and tracer.stat differences for
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES at that revision. Reassuringly:
./sette_eval.sh -V NO_ICB2 -v NO_ICB1 -R 14886 -q
0 differences from 1 matches. 12 missing from REFERENCE 12 missing from VALID
and:
./sette_eval.sh -V MAIN -v NO_COLL -R 14886 -q
0 differences from 1 matches. 0 missing from REFERENCE 12 missing from VALID
Keeping track of archived results
It is apparent that with all this flexibility comes the risk of losing track of which
revisions have been tested with which configurations. SETTE now includes a
helper script which can table the options available for comparison. E.g.:
./sette_list_avail_rev.sh
Compiler used is : X86_ARCHER2-Cray
List of all avail. rev. in :/work/n01/n01/acc/NEMO/GIT/nemo/sette/NEMO_VALIDATION/MAIN/
is : 21334_522ad4c+ 21335_440ad90+ 21336_0235f28+ 21336_416860f+
Availability for each config.:
------------------------------
GYRE_PISCES : ------------ 21335_440ad90+ 21336_0235f28+ 21336_416860f+
ORCA2_ICE_PISCES : ------------ 21335_440ad90+ 21336_0235f28+ 21336_416860f+
ORCA2_OFF_PISCES : ------------ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
AMM12 : ------------ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
WED025 : ------------ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
ORCA2_ICE_OBS : ------------ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
ORCA2_SAS_ICE : ------------ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
AGRIF_DEMO : ------------ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
SWG : ------------ ------------ ------------ ------------
ISOMIP+ : 21334_522ad4c+ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
OVERFLOW : ------------ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
LOCK_EXCHANGE : ------------ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
VORTEX : ------------ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
ICE_AGRIF : ------------ ------------ 21336_0235f28+ ------------
By default, this lists the options in the MAIN sub-directory but other parts of the directory tree can be examined using command-line arguments:
sette_list_avail_rev.sh :
list all sette directory and available revisions created with the compiler specified in param.cfg or in the startup file)
-c COMPILER_name :
list all sette directory and available revisions created with the compiler specified
-v sub_dir :
validation sub-directory below NEMO_VALIDATION_DIR
To add a new configuration
creates a new
input_NEW_CONFIG.cfgif you need tar file (if you use same tar file of GYRE, ORCA2_LIM or ORCA2_LIM_PISCES you can use it)add a bloc in one of the
sette_reference-configuration.shorsette_test-cases.shscriptadd your configuration to the list in
param.cfg